Wando Abalone Information
Brief
 Introduction
Cultivation in an inclosing net has started has started in earnest with administration of license in 2001 since the technology was developed in 2000 at Heuksando. It was introduced to Wando in 2000. The Abalone production has rapidly increased since Abalones produced by cultivation in an inclosing net was distributed in 2003.
Introduction
Cultivation in an inclosing net has started has started in earnest with administration of license in 2001 since the technology was developed in 2000 at Heuksando. It was introduced to Wando in 2000. The Abalone production has rapidly increased since Abalones produced by cultivation in an inclosing net was distributed in 2003.
- ProductionRegular cultivation started from 2003 and the production has increased steadily every year. The production in 1994 was just approximately 100 ton but increased to 6,400 ton in 2009.
- Main producing areaWando is main producing area so the production in Wando occupied 80% of domestic production. The number of cultivation facilities accounting for 80%(293,183 spaces) of total spaces(365,227 spaces) disperses on this area.
- CultivationAbalones are mostly cultivated by a marine inclosing net. Fatness time is from February to July then in breeding season fatness time starts to be low and reaches its lowest on September to October. The growth of Abalone varied in different areas, In northern area shell takes 5-7 years to grow to 7.5cm but in southern area it takes 4-6 years to grow to 11cm.
- ShipmentDividing Abalones on basis of growth speed by 17 steps, basically They are traded according to 1kg unit by size. Abalones shipped from producing area are distributed through mid-distributors to wholesale and retail market or exported to global market.
- Living SpeciesThe Abalone cultivated in Korea is ‘Abalone(ChamJeonbok)’ and scientific name is ‘haliotis discus hannai’. They are distributed widely through eastern-western-southern sea and breeding season is from June to July.
<Abalone Production Status in the World by each country>
(Unit : Tone, %)| separation | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 25.863 | 33,701 | 36,378 | 40,091 | 46,936 | 55,504 | 100.0 |
| China | 9,810 | 13,515 | 15,460 | 18,921 | 25,324 | 33,010 | 59.5 |
| Australia | 5,192 | 5,838 | 5,984 | 5,517 | 5,470 | 5,320 | 9.6 |
| Korea | 1,159 | 1,361 | 2,264 | 3,220 | 4,609 | 5,318 | 9.6 |
| Chile | 3,091 | 3,858 | 3,613 | 4,297 | 3,311 | 3,725 | 6.7 |
| Peru | 670 | 2,906 | 3,531 | 2,359 | 2,543 | 2,757 | 5.0 |
| Japan | 2,181 | 1,996 | 1,768 | 1,976 | 2,063 | 1,700 | 3.1 |
| South America | 921 | 1,018 | 1,058 | 1,045 | 906 | 1,098 | 2.0 |
| others | 5,941 | 6,223 | 5,526 | 5,777 | 5,679 | 5,374 | 9.7 |
Data : FAO, in 2008
- Total production of Abalone in the world reached approximately 56,000 ton. China accounts for 60% of the Production among countries and has the highest output in 2008.
- In sequence, Australia gets 10%, Korea 10%, Chile 7%, Peru 5%.
<Abalone Export Status in the World by each country>
(Unit : Tone, %)| separation | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 5,633 | 5,459 | 4,748 | 4,977 | 5,403 | 100.0 |
| Australia | 2,556 | 2,626 | 2,625 | 2,674 | 2,536 | 46.9 |
| New Zealand | 758 | 788 | 721 | 762 | 880 | 16.3 |
| Thai | 98 | 27 | 13 | 15 | 579 | 10.7 |
| Taiwan | 943 | 450 | 470 | 458 | 398 | 7.4 |
| Korea | 21 | 70 | 214 | 416 | 377 | 7.0 |
| Chile | 293 | 372 | 407 | 429 | 327 | 6.6 |
| USA | 216 | 215 | 169 | 157 | 154 | 2.9 |
| Japan | 75 | 65 | 50 | 42 | 69 | 1.3 |
| Malaysia | 1 | 52 | 7 | 23 | 51 | 0.9 |
| others | 672 | 794 | 72 | 1 | 2 | 0.0 |
Data : FAO, in 2007
- Total export of Abalone in the world reached approximately 50,400 ton. Australia accounts for 47% of the Production among countries and has the highest export in 2007.
- In sequence, New Zealand gets 16%, Thai 11%, Taiwan 7%, Korea 7%.
Distribution
- In northern area distribution of cold current species(Abalone-Chamjeonbok), in southern area distribution of hot current species(Maljeonbok, KKamakjeonbok, Sieboldjeonbok, Obungaji) with isotherm whose water temperature becomes 12℃ in the layer of 25m depth on February as a border
- Depth for Cultivation : 2~40m
- Living Water Temperature(Optimum Temperature) : 10~23℃(적수온 15~20℃)
Habitude
- Abalone has outside-ocean feature, generally spreads on rock zone with a lot of waves and place with rich algae and fresh water.
- Abalone mostly tends to live on specified spot and prefers to dark rock structures.
- Food habits : Herbivorous (consumed brown algae such as seaweed, kelp, gulfweed and in addition to green algae including green laver and red algae including curely moss)
- Breeding Season : Cold current species(July to September), Hot current species(September to next January)
- Feed
- the Young: adhesion diatoms
- Adult : algae including seaweed and laver - Feed Activity(Eating) : influenced highly by water temperature
- week fasting state and the activity becomes very slack under the condition of the water temperature below 7 ℃ and above 25 ℃.
- Higher feeding rate and growth rate under the condition when the water temperature becomes higher between 15℃ and 20 ℃.
Cultivation Facilities
- The size of one space for an inclosing net varied depending on areas with respect to cultivation facilities of a marine inclosing net. In Wando, Jindo and Haenam area 2.4x2.4x2.5m small-sized inclosing net occupied most of spaces but in Heuksando area, People are mostly using 2.4x4.8x2.5m medium-sized inclosing net because of partial remodeling of inclosing net for cultivation of fishes to reduce facilities costs of inclosing net for Abalones.
- The inclosing net should be installed consistent with the drift of a current as a note also gap among inclosing nets should be at least more than 10m for smooth stream of a current.
Cultivation Environment
- The following picture displays change of the water temperature as crucial environment element for cultivation of Abalone in Jindo, Wando and Heksando from July 1st 2006 to June 20th 2007. In Wando, the scope of cultivation water temperature is 8.5-25.8℃ and remains 16.1±5.2℃ as average.
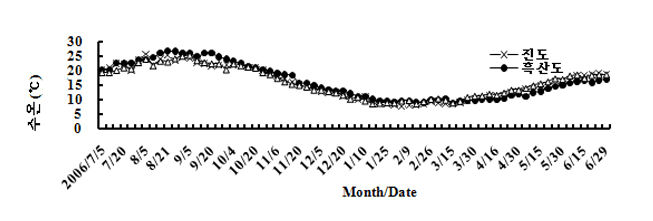
<Change of Water Temperature in Jindo, Wando and Heuksando in July 2006 to June 2007 for a year>
| Country | Water Temperature(℃) | Total | '06.7 | '06.8 | '06.9 | '06.10 | '06.11 | '06.12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wando | Scope | 8.5~25.8 | 19.0~23.0 | 21.9~25.3 | 20.5~25.8 | 18.7~22.7 | 13.5~19.5 | 10.4~13.5 |
| Average±Deviation | 16.1±5.2 | 20.4±0.9 | 23.7±0.9 | 21.0±1.4 | 21.0±1.2 | 16.0±1.6 | 12.2±1.0 | |
| Jindo | Scope | 5.8~25.8 | 19.5~23.5 | 21.5~25.8 | 21.3~25.0 | 18.6~23.0 | 13.6~18.7 | 7.2~13.2 |
| Average±Deviation | 15.4±5.8 | 21.2±1.1 | 23.9±1.2 | 22.6±1.2 | 20.8±1.2 | 16.0±1.5 | 11.0±1.8 | |
| Heuksando | Scope | 8.8~29.8 | 19.3~23.7 | 23.5~27.2 | 23.7~26.3 | 20.1~29.8 | 14.8~19.6 | 12.0~14.7 |
| Average±Deviation | 16.8±5.7 | 21.9±1.4 | 25.5±1.3 | 25.4±0.7 | 21.9±1.9 | 17.1±1.7 | 13.2±0.8 |
| Country | Water Temperature(℃) | '07.1 | '07.2 | '07.3 | '07.4 | '07.5 | '07.6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wando | Average | 8.5~11.0 | 8.7~10.7 | 9.0~11.4 | 10.6~13.6 | 13.5~17.5 | 17.0~19.6 |
| Average±Deviation | 9.5±0.7 | 9.6±0.6 | 10.1±0.8 | 12.3±0.9 | 15.7±1.2 | 18.5±0.6 | |
| Jindo | Scope | 6.8~11.0 | 5.8~9.0 | 6.5~10.3 | 8.5~13.0 | 12.7~16.7 | 15.4~19.7 |
| Average±Deviation | 8.4±0.9 | 7.6±0.9 | 8.4±0.9 | 11.1±1.1 | 4.6±1.2 | 18.1±0.9 | |
| Heuksando | Scope | 9.1~11.9 | 8.9~10.0 | 8.8~10.4 | 10.0~12.1 | 11.2~15.4 | 15.5~17.3 |
| Average±Deviation | 10.4±0.9 | 9.5±0.3 | 9.7±0.3 | 10.8±0.7 | 13.3±1.3 | 16.3±0.5 |
Supply Period and Amount by kinds of feed
- In the case of first-half seaweed, the seaweeds for Abalone’s feeds are exploited as picking raw seaweed from the middle of November by installing seaweed cultivation facilities. In the case of second-half seaweed, are exploited for Abalone’s feeds by picking from the beginning of December to the end of March as installing seaweed cultivation facilities.
- In large-sized aquafarm, it feeds to an inclosing net by using crane equipped on managing ship.
- In the case of first-half seaweed, the delay for the young feeding period will be caused by unstable feeding owing to swept or eliminated leaves of seaweeds occurring from high water temperature or the phenomenon which the surface of water becomes milky-blue or milky green after the middle of September
- Raw seaweeds or sea tangles are supplied as feed of Abalone in cultivation of an inclosing net but salted seaweeds, sea tangles or/and dried seaweeds are supplied during the period when the raw feeds are not supplied. The term of supply is 7-10 days and 80kg/1 space will be appropriate but if feeding the same amount as usual in high water temperature, growth of Abalone becomes slow and diseases might be affected because the flow of a current would be interfered with the rest of feeds and cultivation environment would be worse, it is recommended that you supply 30% reduced amount in comparison with normal amount by frequent.
- Even though reported the value of seaweed as feeds of the young is better than that of sea tangles, it is impossible to supply seaweeds all the year that sea tangles, salted sea weeds, salted sea tangles and dried sea tangles are supplied.
- The appropriate method for feed is to supply reasonable amount for feed to make once supplied feed the amount to the extent that will not become corrupt after monitoring the amount of intake
- The higher water temperature is within the scope of the possible temperature for growth and the smaller shell is, the higher amount of feed intake by weight of Abalone units is. In contrary, the lower and the bigger, the lower amount of feed intake.
Kinds of Abalones
The kinds of Abalones which live in Korea are 5 kinds including Chamjeonbok of cold current Abalones in northern area and Maljeonbok, KKamakjeonbok, Sieboldjeonbok, Obungaji of hot current Abalones in southern area with isotherm whose water temperature becomes 12℃ in the layer of 25m depth on February as a border.
 ChamjeonbokThe habitat is the depth of 4-5cm in southern area. Its length is less than 13cm. it could not grow too large. And it takes 4-5 years to grow to 7cm.
ChamjeonbokThe habitat is the depth of 4-5cm in southern area. Its length is less than 13cm. it could not grow too large. And it takes 4-5 years to grow to 7cm.  MaljeonbokMaljeonbok generally lives on rocks which depth of 10-20m in Jeju, Korea. It is average that Maljeonbok whose length is 10cm, width is 10cm and weight is 400g, occasionally there are one whose weight is 1kg. It just only takes 2-2.5 years to growth 7cm.
MaljeonbokMaljeonbok generally lives on rocks which depth of 10-20m in Jeju, Korea. It is average that Maljeonbok whose length is 10cm, width is 10cm and weight is 400g, occasionally there are one whose weight is 1kg. It just only takes 2-2.5 years to growth 7cm.  ObunjagiEven though Obunjagi is a kind of Abalone, no matter how big it can't exceed length of 7-8cm and smaller than Abalones due to the limit of growth, there are some opinions to differentiate Obunjagi from Abalones.
ObunjagiEven though Obunjagi is a kind of Abalone, no matter how big it can't exceed length of 7-8cm and smaller than Abalones due to the limit of growth, there are some opinions to differentiate Obunjagi from Abalones.




